How to mange your Python environment with Conda
What is Conda¶
Conda provides package, dependency, and environment management for any programming language. It is available through various distributions, including Anaconda, Miniconda, and Miniforge. The Anaconda Distribution comes with a large number of pre-installed scientific computing libraries, which requires more storage space. Miniconda and Miniforge are lightweight versions of Anaconda, pre-installing only a few essential libraries. The main difference between them is that Miniconda, like Anaconda, is a product of the Conda organization, while Miniforge is managed by the community.
In summary, if you plan to use Conda on a laptop, the lightweight versions (Miniconda or Miniforge) are recommended. However, if you are using a desktop computer, the full Anaconda Distribution is preferred.
Here, we use Anaconda as an example. However, you don't need to worry, as the commands for different distributions are almost the same. For more details, please see the official user guide.
How to Install Anaconda¶
First, you should find a suitable version of Anaconda on the official website. In most cases, Anaconda3-2023.09-0-Linux-x86_64.sh and Anaconda3-2023.09-0-Windows-x86_64.exe are suitable.
Linux¶
You can download the above file with wget command:
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2023.09-0-Linux-x86_64.sh
Then run this script and press Enter to start the installation.
bash Anaconda3-2023.09-0-Linux-x86_64.sh
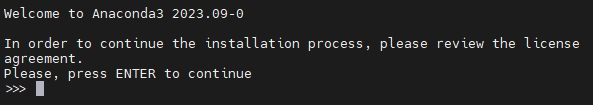
The End User License Agreement - Anaconda Distribution is displayed, enter q to skip reading the agreement and enter yes to accept the license terms.
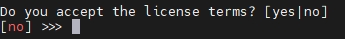
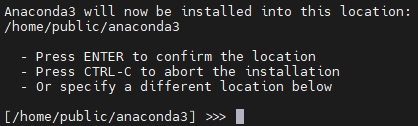
Then you can specify the installation location instead of using the default one.
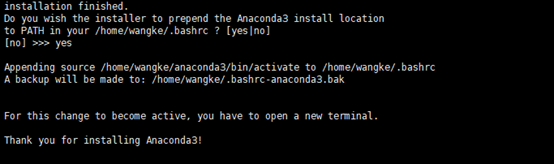
Finally, enter yes to add the Anaconda path into environment.
You can use conda -V to check whether Anaconda has been successfully installed.
Windows¶
You can simply install it as you would any Windows software using the .exe file.
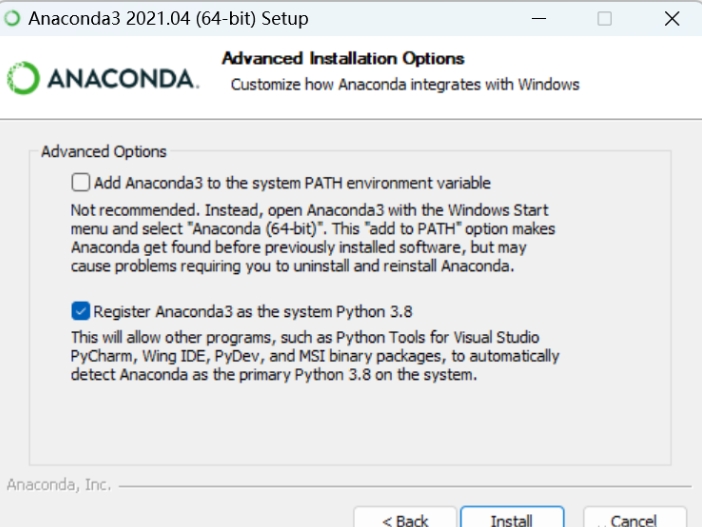
The only thing you need to pay extra attention to is shown in the following image.
If you don't want to configure the environment manually, you should select these two options.
Add Mirror Sources¶
When using Anaconda to manage Python data science and scientific computing environments, network issues can sometimes cause package downloads from the default international sources to be very slow or even fail. Therefore, using domestic mirror sources can greatly improve download speed and success rates.
For example, you can enter the following command in terminal (Linux) or anaconda promote (Windows) to add Tsinghua mirror
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main/
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/conda-forge/
# To configure Conda to display channel URLs during package searches
conda config --set show_channel_urls yes
You can use conda config --show channels to check the mirror sources that have been added.
Common Conda Commands¶
- Install a package into an environment:
conda install Package_Name - List all installed packages in the current environment:
conda list - Create a new environment:
conda create --name YOU_ENV_NAME, e.g.: useconda create --name py38 python==3.8to create an environment named py38 with Python version 3.8. - Activate an environment:
conda activate --name YOU_ENV_NAME - Deactivate the current environment:
conda deactivate - List all environments:
conda env list